Science behind the project
What is its role of HsClpP in cells?
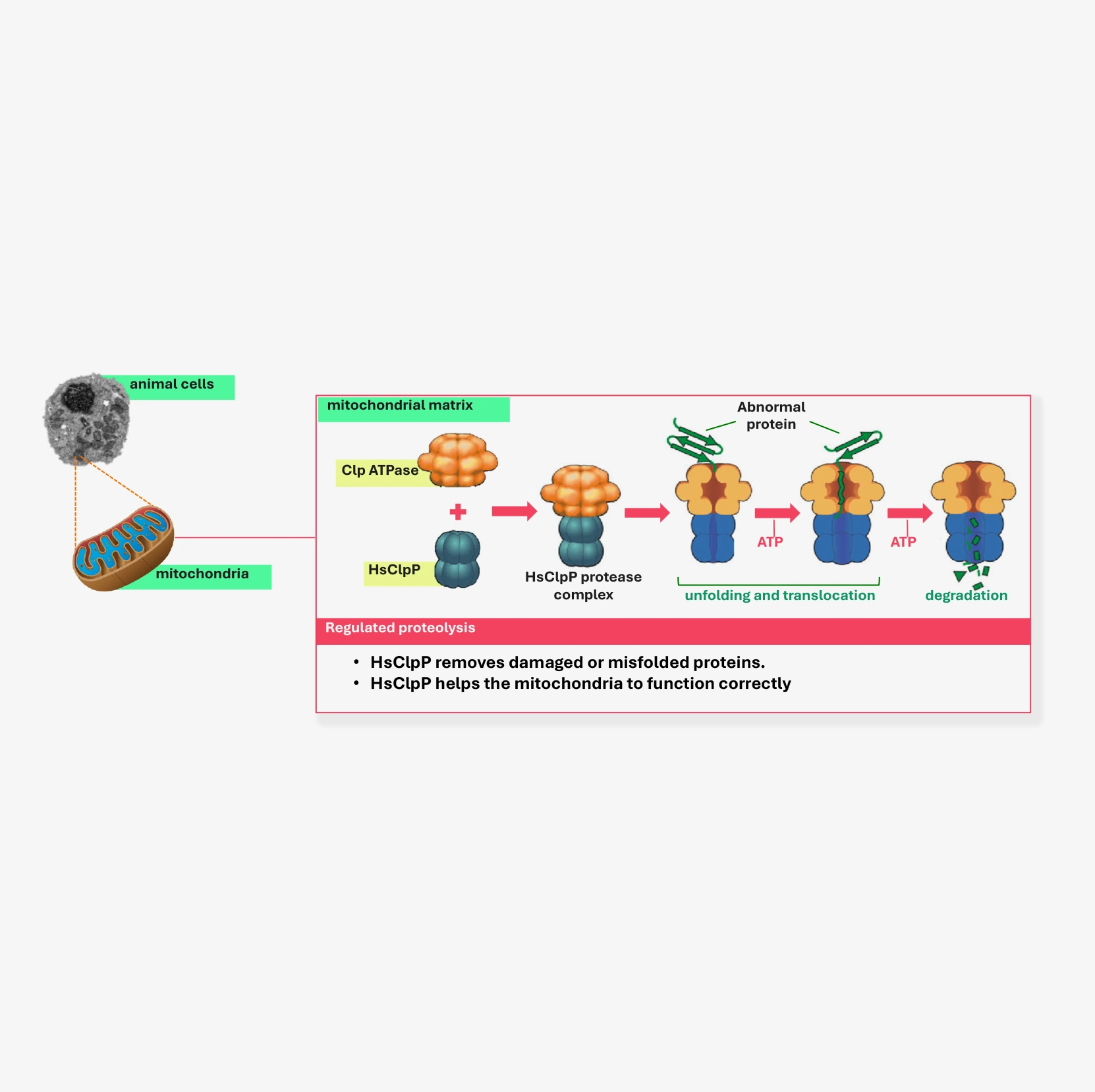
- The human caseinolytic protease P (HsClpP) helps us maintain the correct balance of proteins within our cells.
- In particular, HsClpP degrades proteins that are mis-folded or dysfunctional in the mitochondria.
- Seven (7) HsClpP proteins bind together to form a donut like structure, and two of these donuts stack one on top of the other to form a barrel shaped structure with a central pore (see figure opposite).
- These barrel forms the ClpP can only degrade small peptides. However, chaperone proteins (ClpX) help guide mis-folded or dysfunctional proteins into the HsClpP pore and activate it, resulting in their degradation.
- Cancer cells generate large quantities of proteins to support their prolonged growth/proliferation phases and are therefore very dependent on proteases to maintain protein homoeostasis.
- Due to this dependence on proteases, protein levels of HsClpP are generally far higher in cancer cells compared to normal cells.
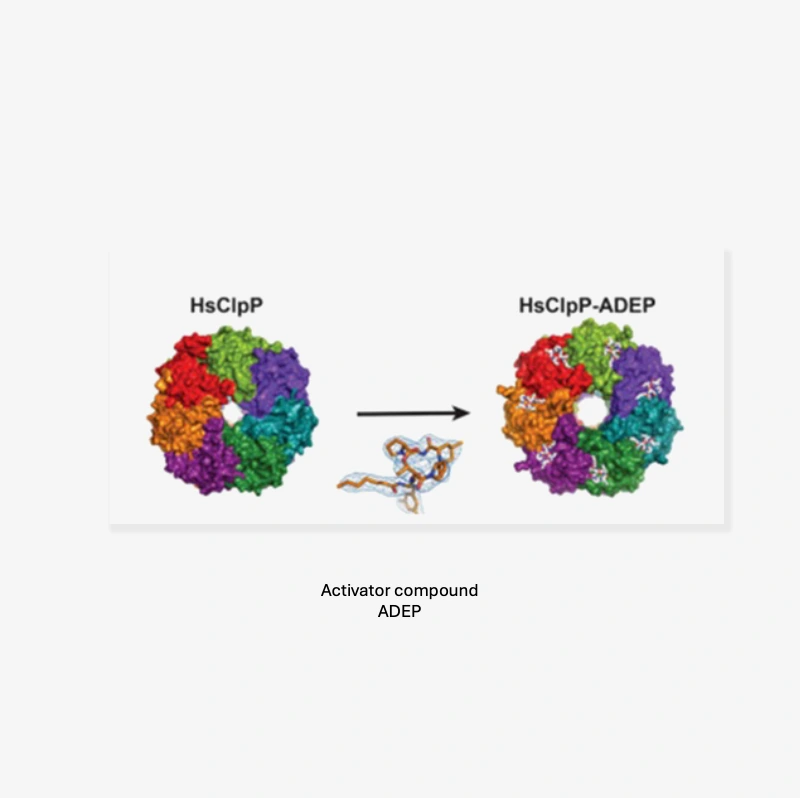
- Agents that can bind and activate HsClpP, cause significant conformational changes which lead to two main events:
- The chaperones can no longer bind to the tetradecameric HsClpP system
- The axial pore is stabilized in an open, and active position
(see figure opposite).
Activation of HsClpP causes the central pore to open
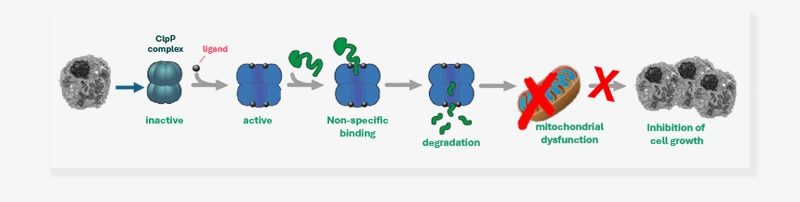
Activated HsClpP acts independently of the chaperones and degrades a greater range of proteins in an uncontrolled manner. This often leads to the degradation of respiratory chain complexes, activation the JNK/c-Jun pathway, and inducing an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response. This response consequently leads to the activation of apoptopic pathways and causes growth arrest in cancer cells (see figure below).
Scientific publications related to HsClpP activators
General introduction: HsClpP activators as potential anti-cancer agents
1. The Role of ClpP Protease in Bacterial Pathogenesis and Human Diseases
Bhandari, V., et al., ACS Chem Biol 2018, 13, 1413-1425;
3. Human ClpP protease, a promising therapy for diseases of mitochondrial dysfunction.
Luo, B., et al., , Drug Dis.Today., 2021 26(4), 968-981; http://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2021.01.007
2. Substrates and interactors of ClpP protease in the mitochondria
Mabanglo, MF., et al., Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2022, feb 66:102078;
4. Mitochondrial HsClpP serine protease-biological function and emerging target for cancer therapy.
Nouri K, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(10):841. Published 2020 Oct 9. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-03062-z.
Recent publications demonstrating the effects of some HsClpP activators in different types of cancers
1. Discovery of CLPP-1071 as an Exceptionally Potent and Orally Efficacious Human ClpP Activator with Strong In Vivo Antitumor Activity
Chen, B., et. al., J. Med.Chem., 2024 https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c01605
2. Rational Design of a Novel Class of Human ClpP Agonists through a Ring-Opening Strategy with Enhanced Antileukemia Activity.
Xiang, X., et. al., J. Med.Chem., https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00338
